Osteoporosis
- Bone Modeling and Remodeling
- Remodeling : osteoclast, osteoblast
- remodeling cycle: cement line
- Control of remodeling cycle
- RANKL/RANK
- cytokine eg. osteoprotegerin (OPG)
- Bone VS age
- Infant
- endochondral ossification at epiphyseal growth plate
- Child to adult 30 years old
- harversian canal ,intertrabecular space
- peak bone mass
- Adult more than 30 years old
- Post menoposal
- Loss trabecular bone mass
- Bone density evaluation
- X-ray
- Rickets,
- Osteomalacia
- metastatic bone
- quantitative CT scan
- bone mass density test
- dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
- biochemical test
- serum calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase
- Osteocalcin (Gla protein)
- B-cross lap
- P1NP (Procollagen type I)
- Type
- Primary Osteoporosis
- Type I: Post menopausal osteoporosis
- Type II: Senile (Involutional) osteoporosis
- Secondary Osteoporosis
- steroid induce
- immobilization
- chronic disease
- Post-menopausal osteoporosis
- Risk Factor
- White, asian
- Family history
- Miss mense
- Excessive exercise
- Anorexia
- Low BMI
- Oopholectomy
- Smoking
- Drinking
- Symptom
- Back pain
- Kyphosis
- Decrease height
- Low energy fracture
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Life style modification
- Ca, vitamin D
- Hormonal replacement therapy (HRT)
- Bisphosphonate
- Parathyoid hormore
Benign neoplasm of bone
- Definition
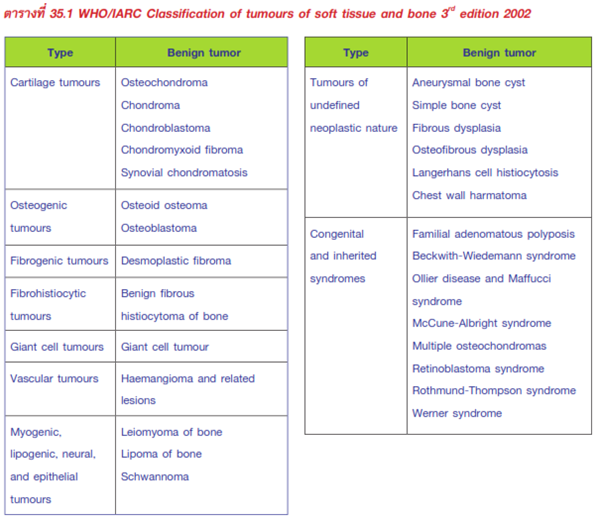
- Classification: WHO/IARC Classification
- Presentation
- Mass, Pain, Deformity, Pathologic fracture, accidental finding
- Site, Size, color, consistence, tenderness, fixed
- Benign neoplasm of bone
- Screlotic border
- No cortical involvement
- No soft tissue extension
- MRI
- Biosy
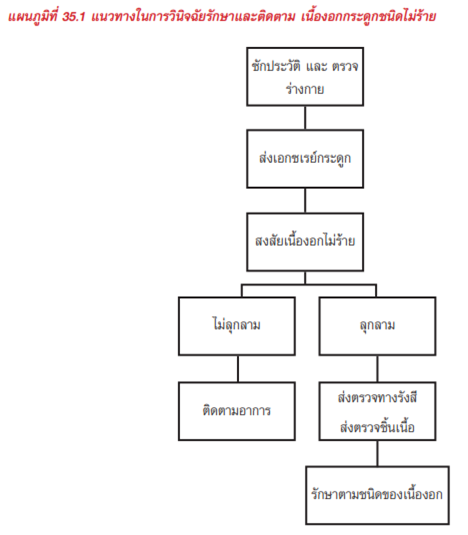
- Physical examination
- Radiographic appearance
- Further investigation
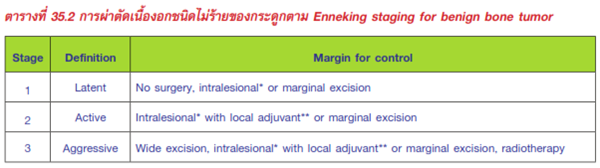
- Treatment: Enneking staging for benign bone tumor
- Latent
- Active
- Aggressive
- - Follow up
Malignant neoplasm of bone
- Definition
- Classification: WHO/IARC Classification
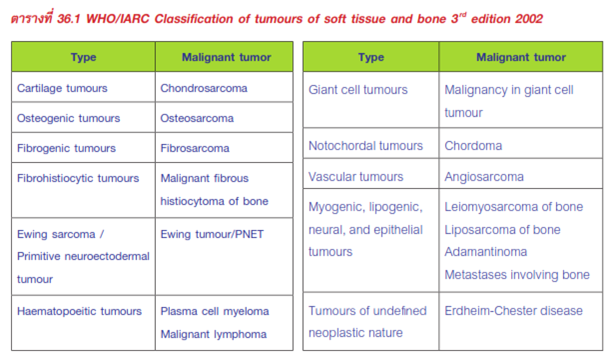
- Presentation
- Mass, Pain, Deformity, Pathologic fracture, accidental finding
- Site, Size, color, consistence, tenderness, fixed
- Moth eaten, permeative
- Cortical involvement
- Periosteal reaction
- Soft tissue extension
- MRI, CT chest, chest x-ray, bone scan
- Serum CBC, Calcium, Phosphate, Parathyroid hormone, ESR, CRP, Liver function test, BUN, Creatinine, Urinalysis, Urine Bence-Jone protein, Serum electrophoresis, PSA
- Biosy
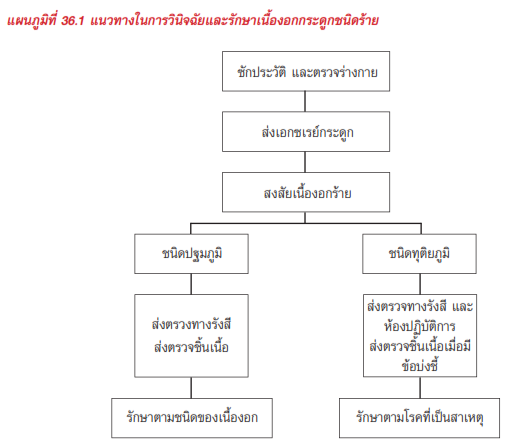
- Physical examination
- Radiographic appearance
- Further investigation
- Treatment: Enneking staging for Malignant bone tumor
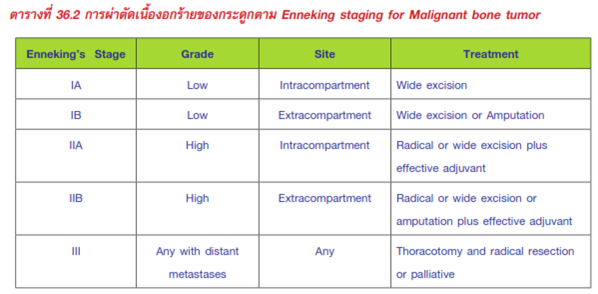
- Tumor resection
- Bone & soft tissue reconstruction
- Follow up
Metastatic bone diseases
- Definition
- Epidemiology
- Breast, prostate, kidney, lung, Thyroid
- Pain
- Pathologic fracture
- Bone
- Moth eaten, permeative
- cortical involvement
- Periosteal reaction
- Soft tissue extension
- CXR
- Bone scan
- CT scan chest, abdomen ,pelvis
- PET scan
- U/S thyroid, thyroid scan
- Biopsy
- Open
- Core needle
- ESR , alkaline phosphatase
- PSA, CEA, CA19-9, AFP,CA125
- serum protein electrophoresis
- serum calcium, phosphate, PTH, vitamin D
- Presentation
- Physical examination
- Radiographic appearance
- Further investigation
- Laboratory study
- Treatment
- Pain control
- Radiation therapy
- Hormone therapy
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- Pathologic fracture
- Prophylactic fixation
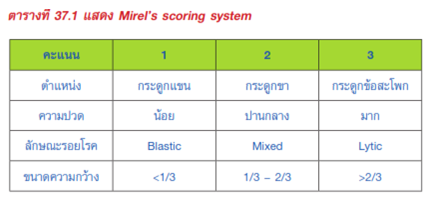
- Mirel’s scoring system